Epyc "Turin" server processor: AMD wants to outdo Intel even further
AMD CEO Lisa Su gives a somewhat confusing outlook on the Zen 5 generation of Epyc processors for servers, which will compete against Intel's Xeon 6 end of 2024.
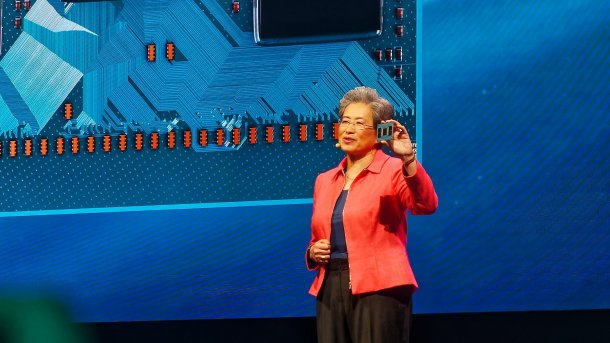
AMD CEO Lisa Su presents the Zen 5 generation server CPU "Turin" with 192 cores.
(Image: c't / chh)
At Computex 2024 in Taipei, AMD CEO Lisa Su personally presented an AMD Epyc "Turin" with up to 192 CPU cores of the Zen 5 generation for the first time in public. However, the Turin Epycs will not be launched on the market until later this year. Lisa Su did not reveal exactly when. And although she explained that the Turin with 192 cores is produced using "3-nanometer technology" and consists of up to 13 chiplets, she then showed several benchmarks of a Turin version with 128 cores. This was often more than three times as fast as Intel's current Xeon Platinum 8592+, a 64-core of the current Emerald Rapids generation.
Videos by heise
Opponent: Xeon 6
The confusion with 192 and 128 cores and the benchmark opponents can probably be explained by the fact that AMD is targeting the upcoming Intel Xeon 6 in the "Sierra Forest" and "Granite Rapids" variants with Turin. Intel has already confirmed that Sierra Forest will have up to 288 E-cores. Lisa Su therefore named Turin's 192 cores and 384 threads in order to outdo the competition.
However, this is presumably a version of Turin with the slimmed-down Zen 5c cores. According to speculation, new Core Complex Dies (CCDs) from the TSMC N3 production technology could each contain up to 16 Zen 5c cores. Twelve such chiplets together with an I/O die (IOD), which as before comes from TSMC N6 production, result in a 192-core processor that fits into the same SP5 socket as the Epyc 9004 "Genoa".
(Image: c't / chh)
However, Intel's second Xeon 6 version Granite Rapids is expected to have up to 128 of the more powerful P cores when fully expanded. That is twice as many as Intel was previously able to offer per CPU version. The benchmarks of a "Turin 128c", which Lisa Su showed, shot against this upcoming 128-core.
This is also supported by the fact that the 128-core outperformed the current Xeon by a factor of 3. This is apparently intended to show that even if Intel doubles the number of cores, the Epyc remains faster.
In her Computex keynote, however, Lisa Su did not differentiate between Zen 5 and Zen 5c.
Presumably 16 CCDs for 128x Zen 5
AMD uses the same CCDs for the previous Zen 4 Epycs 9004 from TSMC's N5 production as for the Ryzen 7000, so it stands to reason that AMD uses the same CCDs for Turin with "normal" Zen 5 cores as for the Ryzen 9000.
(Image: c't / chh)
Today, Lisa Su also presented the Ryzen 9000 with significantly improved Zen 5 technology and still eight cores per CCD. However, she did not mention the production technology. According to speculation, AMD could rely on TSMC N4P; this manufacturing process is closely related to TSMC N5, but offers advantages in terms of packing density and efficiency. However, 16 CCDs would then be required for a Turin with 128 Zen 5 cores, i.e. 17 chiplets including IOD.
AMD confirmed to heise online that the Ryzen 9000 CCDs are manufactured using 4-nanometer technology. Unlike the Ryzen AI 300, which also has Zen 5 cores, the Ryzen 9000 CCDs do not contain any NPUs.
No major update is necessary for the IOD because the Turin Epycs will continue to run in SP5 boards.
Empfohlener redaktioneller Inhalt
Mit Ihrer Zustimmung wird hier ein externer Preisvergleich (heise Preisvergleich) geladen.
Ich bin damit einverstanden, dass mir externe Inhalte angezeigt werden. Damit können personenbezogene Daten an Drittplattformen (heise Preisvergleich) übermittelt werden. Mehr dazu in unserer Datenschutzerklärung.
(ciw)