Open-source humanoid robot you can build yourself for 5000 US dollars
Humanoid robot technology should be accessible to as many people as possible. Researchers at UC Berkeley have developed a robot that can be replicated.
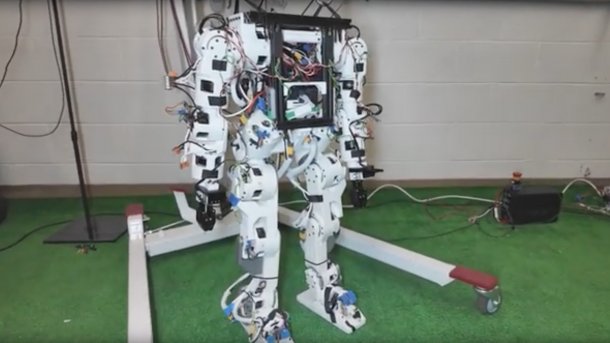
The Berkeley Humanoid Lite may be headless, but it still has a certain amount of intelligence.
(Image: UC Berkeley (Screenshot))
A team of scientists at the University of California Berkeley (UC Berkeley) has developed a humanoid robot that is constructed from standard electronic parts and whose structural parts can be printed using a conventional 3D printer. The cost of the robot is comparatively low at 5000 US dollars. Resourceful hobbyists can easily replicate it. With the robot, the researchers want to enable a broad base to get involved with humanoid robot technology.
It doesn't take much to assemble the Berkeley Humanoid Lite. All it takes is a few tools, skill, money and a desktop 3D printer with a print area of 200 mm x 200 mm x 200 mm. The latter can be used to print the structural parts to give the robot a body. A few aluminum parts to support the structure have to be made by yourself. The required electronic components are freely available in almost every electronics store.
Empfohlener redaktioneller Inhalt
Mit Ihrer Zustimmung wird hier ein externes YouTube-Video (Google Ireland Limited) geladen.
Ich bin damit einverstanden, dass mir externe Inhalte angezeigt werden. Damit können personenbezogene Daten an Drittplattformen (Google Ireland Limited) übermittelt werden. Mehr dazu in unserer Datenschutzerklärung.
The finished robot is 80 cm tall and weighs 16 kg. A great deal of development work went into the cycloidal gears, which are used by electric motors to move the robot's joints. This type of gearbox is characterized by a high torque, is compact and, in the form specially developed for the robot, should also be less susceptible to wear. In addition, it is relatively inexpensive to produce in-house. A total of 22 of these cycloidal gears are used in the robot to move the arms, legs and torso, for example.
Humanoid robot capable of learning
The robot can be used in various ways. For example, it can be moved by remote control and can run and jump, pick up and place objects with its hands and much more. However, it can also be trained to perform actions independently. This can be done, for example, by specifying sequences via teleoperation, but also through simulations, the training results of which are then transferred to the robot. The scientists at UC Berkeley have tested that this works and carried out a whole series of experiments. This led, for example, to the development of motion control using reinforcement learning (RL).
The instructions for building and operating the humanoid robot are available as open source on a GitHub project page. Interested parties can find freely available designs, CAD files for 3D printing the structural parts as well as parts lists and assembly instructions with tips on assembly. The programming code is also available with explanations of how the robot can be used in practice. The study "Demonstrating Berkeley Humanoid Lite: An Open-source, Accessible, and Customizable 3D-printed Humanoid Robot", which has been preprinted on Arxiv, provides further details about the project.
Videos by heise
"By making the hardware design, embedded code, and training and deployment frameworks fully open-source and accessible worldwide, we aim to take a decisive step towards democratizing the development of humanoid robotics with Berkeley Humanoid Lite," the researchers explain the project.
(olb)