Raspi competition: Qualcomm swallows Arduino and presents single-board computer
The single-board computer Arduino Uno Q gets a Qualcomm processor. It enables projects similar to a Raspberry Pi.
(Image: Arduino)
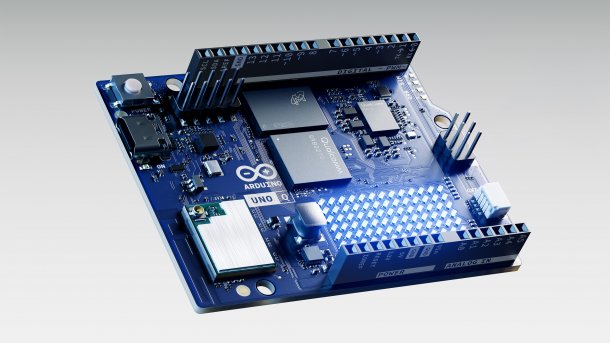
Qualcomm takes over Arduino, a manufacturer known for its microcontroller boards. Qualcomm is presenting its first single-board computer for DIY projects directly on the occasion of the takeover: the Arduino Uno Q. Whereas previous Uno boards only had small microcontrollers for simple tasks, the Uno Q comes with a chip duet consisting of a microcontroller (MCU) and microprocessor (MPU), so that Linux, for example, can run independently on the board.
The MCU in the form of the STMicroelectronics STM32U585 is already significantly faster than the Renesas RA4M1 on the Arduino Uno R4. The new version is based on the ARM core Cortex-M33 with 160 MHz (Uno R4: Cortex-M4, 48 MHz).
Arduino Uno Q (14 Bilder)

Arduino
)From October and 39 Euro
Qualcomm's Dragonwing QRB2210 is also on the board. It contains four Cortex-A53 ARM cores that run at 2.0 GHz. There is also an integrated graphics unit and additional blocks such as image signal processors. Arduino and Qualcomm are also promoting the board for AI applications (Edge AI).
The QRB2210 processor does not have an independent AI unit, but the CPU and GPU should be sufficient for some AI algorithms, such as image recognition. Useful for this: The QRB2210 can control two image sensors with 13 megapixels each or a single 25 megapixel sensor. A hardware decoder and encoder can handle H.265 and H.264 for 1080p videos at 30 fps.
Arduino is launching a variant with 2 GB of LPDDR4 RAM and 16 GB of NAND flash memory (eMMC) for 39 Euro. It will be available from today and from 25 October. A version with 4 GB RAM and 32 GB flash will be available to pre-order from November for 53 Euro and will follow by the end of the year. A wireless module for Wi-Fi 5 (2.4 + 5 GHz) and Bluetooth 5.0 is always included.
(Image: Arduino)
Old technology with plenty of power by Arduino standards
The Cortex-A53 core design is already 13 years old, but is fast enough for many DIY projects. Back then, it was used as an efficiency core in many smartphone processors. On the CPU side, the Arduino Uno Q is roughly comparable to the Raspberry Pi 3 from 2016. Its Broadcom BCM2837 processor also uses four Cortex-A53 cores, which clock a good deal lower at 1.2 GHz ex works.
The combination of microcontroller and microprocessor appears charming from an efficiency perspective. Arduino Core, based on Zephyr OS, runs on the integrated memory of the STMicro chip. The Qualcomm processor can go to sleep almost completely when its performance is not required. It runs Debian Linux operating systems with upstream support as well as support for Docker and Docker Compose.
The new Arduino App Lab serves as a development environment for the CPU, GPU and MCU. The Arduino developers emphasise that they will continue to rely on open source after the Qualcomm takeover – Hardware components will be released under the CC BY-SA 4.0 licence, software under GPL3 and MPL.
Videos by heise
Few connections
The most significant difference to Raspberry Pi single-board computers lies in the connections. Apart from the GPIO pin headers, the Arduino Uno Q only has a USB-C connection. The manufacturer plans to use a USB hub for the power supply (5 volts, 3 amps), HDMI image output (max. 1680 × 720 pixels with 60 hertz) and peripherals. However, the connection only manages USB 2.0 speed. Alternatively, the Arduino Uno Q receives power via GPIO pins.
There are no independent image outputs, no SD card slot for memory expansion and no PCI Express (e.g. for an SSD). However, Qualcomm and Arduino have provided the underside of the board with new pin headers, for which expansion boards called Arduino Carriers are to be released in the future.
The board design, positioning of the headers (QWIIC, SPI 3V3) and GPIO pin headers remain identical, so that existing housings and additional hardware will continue to fit. The LED matrix is also still included. The Arduino Uno Q is also compatible with the I2C/I3C, CAN, UART, PSSI, JTAG and ADC interfaces.
(Image: Arduino)
Empfohlener redaktioneller Inhalt
Mit Ihrer Zustimmung wird hier ein externer Preisvergleich (heise Preisvergleich) geladen.
Ich bin damit einverstanden, dass mir externe Inhalte angezeigt werden. Damit können personenbezogene Daten an Drittplattformen (heise Preisvergleich) übermittelt werden. Mehr dazu in unserer Datenschutzerklärung.
(mma)